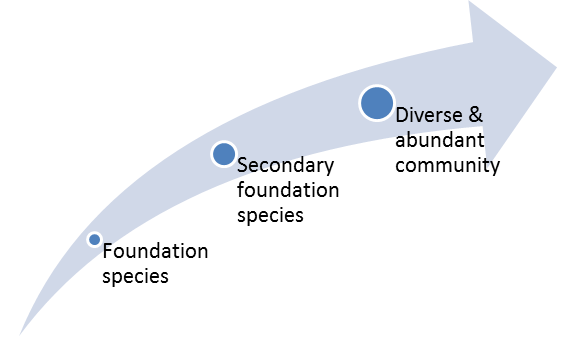
A facilitation cascade describes the order of species arrival in a given environment AND the interactions between these species. The example I’ll use does not involve epiphytes but is adapted from one of the original articles on this idea by Andrew Altieri, Brian Silliman, and Mark Bertness (2007).
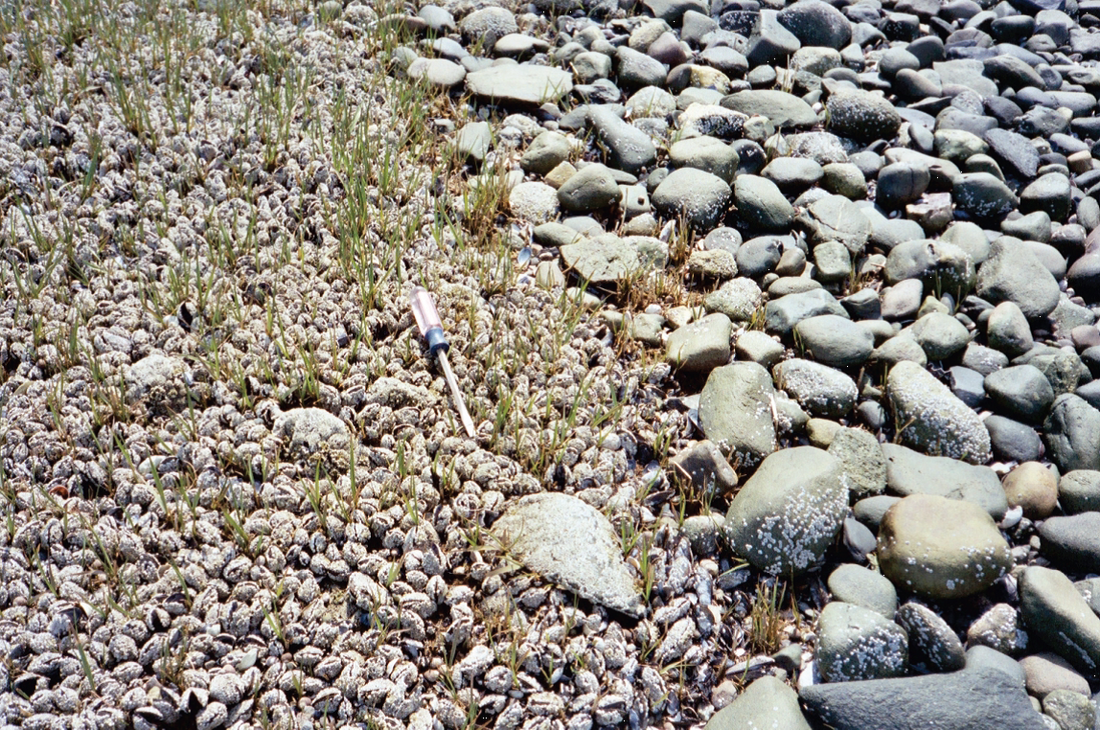
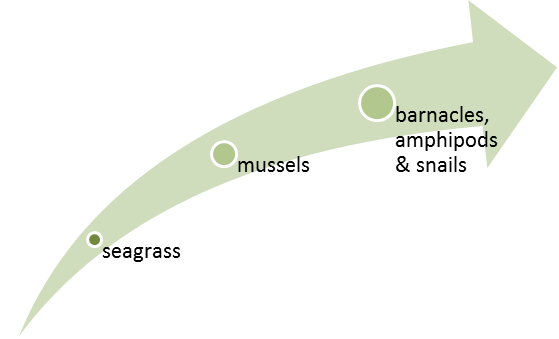
The foundation species provides habitat for a secondary foundation species. Seagrass provides stable substrate for the establishment of mussels that cannot successfully establish on bare rocks.
The combination of foundation and secondary foundation species provides the necessary conditions for many other species to establish and interact. In a coastal system the seagrass and mussels provide substrate and refuge for a diverse and abundant community that includes barnacles, snails and amphipods.
The positive interactions between these species occur in a hierarchical order and, unlike successional theory, the foundation species is not replaced by subsequent species.



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
